Using Lookup in ADF Data Flow
Introduction
SSIS developer, we all know the
importance of Lookup Transform. Here
in ADF, we have two types of Lookup. One is for control flow and other is for
data flow. The behavior of both the lookup is not same. Control flow lookup
provide only record sets but in Data flow we are using it as for looking up
some records from other data sets.
In ADF data flow Lookup feature is more than the SSIS Lookup
Transform. So, in this article we are thinking to demonstrate all the
functionality of ADF Data Flow lookup with a simple example.
Hope it will be interesting.
Case
scenario
We have a Flat file which contains Employee Code, Salary and Bonus
Information. There are multiple Flat files in our Azure BLOB Container.
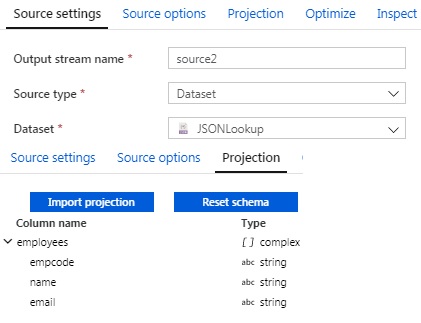
Now we have a JSON file which contains information about Employee
Code, Employee Name and Employee Email.
Now we have to use the Lookup Transform to find the Employee Name
and Employee Email from our JSON file.
About
Data Flow Lookup
Before moving to our actual data flow solution, we must need to
understand every property of Data Flow Lookup.
Primary
stream
The incoming stream of data. This stream is equivalent to the left
side of a join.
Lookup
stream
The data that is appended to the primary stream. Which data is
added is determined by the lookup conditions. This stream is equivalent to the
right side of a join.
Match
multiple rows
If enabled, a row with multiple matches in the primary stream will
return multiple rows. Otherwise, only a single row will be returned based upon
the 'Match on' condition.
Match
on
Only visible if 'Match multiple rows' is not selected. Choose
whether to match on any row, the first match, or the last match. Any row is
recommended as it executes the fastest. If first row or last row is selected,
you'll be required to specify sort conditions.
Lookup
conditions:
Choose which columns to match on. If the equality condition is
met, then the rows will be considered a match. Hover and select 'Computed
column' to extract a value using the data flow expression language.
Non-equi
joins
To use a conditional operator such as not equals (!=) or greater
than (>) in your lookup conditions, change the operator dropdown between the
two columns. Non-equi joins require at least one of the two streams to be
broadcasted using Fixed broadcasting in the Optimize tab.
ADF
Solution Data Flow
Here we are not using any Sync as we are going to display output
in Data Preview mode.
Source –
1
Source –
2
Flatten
Transform
Lookup
Select
with Data Preview
Hope you like it.

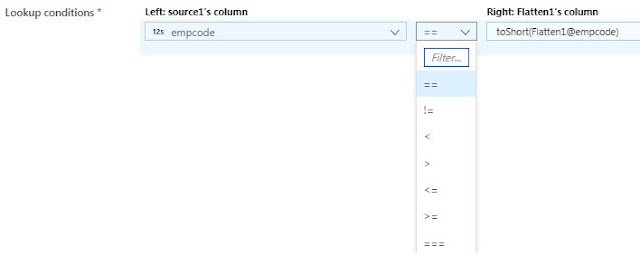







If you have any confusion between == and === operators, here I give you a simple explanation. == check only values and === checks values snd type. Take a simple example:
ReplyDeleteIf(12 == '12') :
pint( 'Yes')
else:
print('No')
---> Yes
If(12 === '12') :
pint( 'Yes')
else:
print('No')
---> No
Hope you understand that.