Working with Python – JSON
Introduction
JSON (Java Script Object Notation) is
very popular nowadays for transmitting data. Here in this Blog Post we are
going discuss about it.
Hope it will be interesting.
Importing
JSON module
Before working with JSON, we have to
import the JSON module in Python.
import json
Parsing
JSON in Python
We can Parse JSON in multiple ways in
Python mentioned bellow.
Parsing
JSON to Dictionary
We
can Parse a JSON using json.loads() methods,
which returns a Dictionary.
Example:
Import json
person = '{"name": "Mayuree",
"languages": ["English", "Bengali"]}'
person_dict = json.loads(person)
print( person_dict)
print(person_dict['languages'])
Output:
{'name': 'Mayuree',
'languages': ['English', 'Bengali']}
['English', 'Bengali']
Here,
person is a
JSON string and person_dic is adictionary.
Read
the JSON File
Now,
it’s time to read a JSON file by python. For example, we are using same JSON
string as a file.
Example:
import json
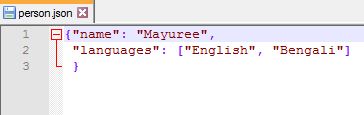
with open('person.json') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print(data)
Output:
{'name':
'Mayuree', 'languages': ['English', 'Bengali']}
In
the above example, the OPEN is used to read the JSON file and JSON.LOAD()
function is used to parse the JSON file into Dictionary.
Converting
Dictionary to JSON string
We
can convert Dictionary to a JSON string using json.dumps()
method.
Example:
Import json
person_dict = {'name': 'Mayuree',
'age': 22,
'children': 2}
person_json = json.dumps(person_dict)
print(person_json)
Output:
{"name":
"Mayuree", "age": 22, "children": 2}
Python
Object and their equivalent conversion of JSON
Hope you like it.

## Here I am not showing to Save data in JSON ... It will be done after complying the file Handeling portion.
ReplyDelete